|
 |
| Saint Kitts (Christopher) and Nevis | |||||
 |
|
||||
|
12 Nov 1493 St. Kitts
and Nevis discovered and claimed
for Spain by Columbus and named them Isla de San Jorge and Isla San Martin (later renamed Isla Nuestra Señora de Las Nieves) respectively. 1623 Saint Christopher (St. Kitts) an English colony. 1625 French also settle on Saint-Christophe. 13 May 1627 - 16 Jul 1702 Island divided into separate English St. Christopher (the center) and French Saint-Christophe both ends) colonies; French colony is under Compagnie de Saint-Christophe rule to 1635. 1628 - 16 Jul 1702 French Saint-Christophe became part of the French Antilles colony (under Martinique). 22 Jul 1628 Nevis becomes English colony (until 1671 subordinated to Barbados). 1635 - 1651 Saint-Christophe Under Compagnie des Îles de l'Amérique rule. 1651 - 1665 Saint-Christophe becomes possession of the Knights of Malta. 1665 Saint-Christophe becomes French colony Apr 1666 - 1671 French occupy entire island under Compagnie des Indes Occidentales rule. 1689 - Jun 1690 French occupy entire island. Jun 1690 - 20 Sep 1697 English occupy entire island. Jan 1671 - 16 Oct 1816 Part of Leeward Islands colony (under Antigua). 1701 - 1704 Under direct rule from Antigua. 16 Jul 1702 British annex French part of the Saint-Christopher island. 22 Feb 1706 - Mar 1706 French occupation of Saint-Christopher island. 24 Feb 1706 Failed French invasion on Nevis. 11 Apr 1713 English possession confirmed by Treaty of Utrecht. 12 Feb 1782 - 03 Sep 1783 Occupied by France. Nevis named as Niévès. 1816 - 1871 Part of Colony of St. Christopher, Nevis, Anguilla and the British Virgin Islands. 1833 - 01 Jan 1960 Part of Leeward Islands colony (under Antigua). 01 Aug 1834 Emancipation Day - ended slavery in the British Empire. 1882 Islands united as Saint Christopher-Nevis-Anguilla. 03 Jan 1958 - 31 May 1962 Part of the Federation of the West Indies (under Trinidad and Tobago). 27 Feb 1967 Associated state 18 Aug 1977 Referendum for secession, organized by the Nevis Reformation Party (total 4,220 persons who voted, 4,193 voted for secession, 14 persons voted no). Declared void by St. Kitts 13 Apr 1980 Renamed Saint Christopher and Nevis. 19 Dec 1980 Final separation of Anguilla. 19 Sep 1983 Independence (Federation of Saint Kitts and Nevis). Nevis granted limited self-government. 13 Oct 1997 Nevis parliament votes for separation from St. Kitts. 10 Aug 1998 Independence referendum fails, 61.7% vote yes however, 66.7% were required for approval. |
|||||
|
|
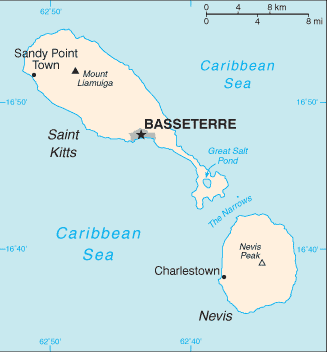
The Federation of Saint Kitts and Nevis is also
known as the Federation of Saint Christopher and Nevis), located in the
Leeward Islands, is a federal two-island state in the West Indies. It is the
smallest sovereign state in the Americas, in both area and population. Today, the Constitution refers to the state as both "Saint Kitts and Nevis" and "Saint Christopher and Nevis", but the former is the one most commonly used. Territorial Dispute: Joins other Caribbean states to counter Venezuela's claim that Aves Island sustains human habitation, a criterion under UNCLOS, which permits Venezuela to extend its EEZ/continental shelf over a large portion of the Caribbean Sea. |
||||
| Historically, the British dependency of Anguilla was also a part of this union, which was then known collectively as Saint Christopher-Nevis-Anguilla. Saint Kitts and Nevis are geographically part of the Leeward Islands. To the north-northwest lie the islands of Sint Eustatius, Saba, Saint Barthélemy, Saint-Martin/Sint Maarten and Anguilla. To the east and northeast are Antigua and Barbuda, and to the southeast is the small uninhabited island of Redonda, and the island of Montserrat, which currently has an active volcano (Soufrière Hills). Saint Kitts and Nevis were among the first islands in the Caribbean to be settled by Europeans. Saint Kitts was home to the first English and French colonies in the Caribbean, and thus has also been titled "The Mother Colony of the West Indies". | |||||
|
There is some disagreement over the name which
Columbus gave to St. Kitts. For many years it was thought that he named the
island San Cristobal, after his patron saint Saint Christopher, the saint of
travelling. However, new studies suggest that Columbus named the island Sant
Yago (Saint James). The name "San Cristobal" was apparently given by
Columbus to the island now known as Saba, 20 miles northwest. It seems that
"San Cristobal" came to be applied to the island of St. Kitts only as the
result of a mapping error. No matter the origin of the name, the island was
well documented as "San Cristobal" by the 17th century. The first English
colonists kept the English translation of this name, and dubbed it "St.
Christopher's Island".
In the 17th century Kit or Kitt, was a common
nickname for the name Christopher and so the island was often informally
referred to as "Saint Kitt's island", which was further shortened to "Saint
Kitts". The current name "Nevis" is derived from a Spanish name Nuestra Señora de las Nieves (The original name was the archaic Spanish "Noestra Siñora delas Neves"), by a process of abbreviation and anglicization. This Spanish name means Our Lady of the Snows. It is not known who chose this name for the island, but it is a reference to the story of a fourth-century Catholic miracle: a snowfall on the Esquiline Hill in Rome. Presumably the white clouds which usually wreathe the top of Nevis Peak reminded someone of the story of a miraculous snowfall in a hot climate. The island of Nevis, upon first British settlement was referred to as "Dulcina," a name meaning "sweet one." Its original Spanish name, "Nuestra Señora de las Nieves", was eventually kept however, though it was soon shortened to "Nevis". |
|||||
|
|||||
|
|||||
|
Monetary standard:
East Caribbean Dollar = 100 cents.
The history of currency in the British colony of St. Kitts closely follows that of the British Eastern Caribbean Territories (Eastern Group) in general. Even though Queen Anne's proclamation of 1704 brought the gold standard to the West Indies, silver pieces of eight (Spanish dollars and later Mexican dollars) continued to form a major portion of the circulating currency right into the latter half of the nineteenth century. From approximately 1750-1830, billon 2 sous of the French colony of Cayenne were countermarked SK' and used on St.Kitts. They were valued at 1-1/2 Pence Sterling. Britain adopted the gold standard in 1821 and an imperial order-in-council of 1838 resulted in St. Kitts formally adopting the sterling currency in the year 1849 (and Nevis in 1858). However, despite the circulation of British coins in St. Kitts, the silver pieces of eight continued to circulate alongside them and the private sector continued to use dollar accounts for reckoning. The international silver crisis of 1873 signaled the end of the silver dollar era in the West Indies and silver dollars were demonetized in St. Kitts in the wake of that crisis. This left a state of affairs, in which the British coinage circulated, being reckoned in dollar accounts at an automatic conversion rate of 1 dollar = 4 shillings 2 pence. From 1949, with the introduction of the British West Indies dollar, the currency of St. Kitts became officially tied up with that of the British Eastern Caribbean territories in general. The British sterling coinage was eventually replaced by a new decimal coinage in 1955, with the new cent being equal to one half of the old penny. |
|||||
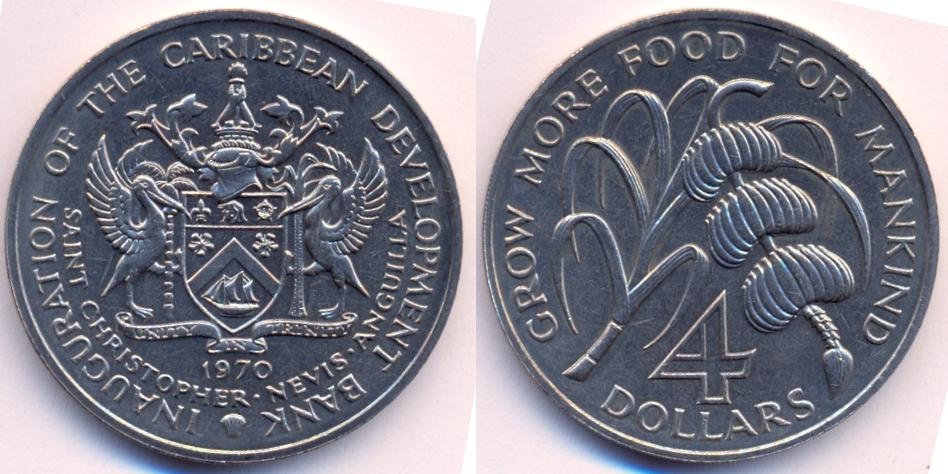
| The East Caribbean dollar (sign: $; code: XCD) is the currency of eight of the nine members of the Organisation of Eastern Caribbean States (the one exception being the British Virgin Islands). It has existed since 1965, being the successor to the British West Indies dollar, and it is normally abbreviated with the dollar sign $ or, alternatively, EC$ to distinguish it from other dollar-denominated currencies. The EC$ is subdivided into 100 cents. It has been pegged to the United States dollar since July 07, 1976 and the exchange rate is US$1 = EC$2.70. Six of the states using the EC$ are independent states: Antigua and Barbuda, Dominica, Grenada, Saint Kitts and Nevis, Saint Lucia, and Saint Vincent and the Grenadines. The other two are British overseas territories: Anguilla and Montserrat. Commemorative coins were produced by Saint Kitts and Nevis in 1970, 1982, 1983, 1985 and 1988. | |||||
| Saint Kitts and Nevis commemorative coins | |||||
|
|||||
| Countries / Territories | |||||
| Chiefa Coins | |||||