|
 |
| Saint Lucia | |||||
 |
|
||||
|
13 Dec 1502 Discovered by Christopher Columbus and claimed for Spain, named Isla de Santa Lucia. 23 Aug 1605 - Sep 1605 First attempted English settlement. 1638 - Aug 1640 Second attempted English settlement. 1643 French colony (Sainte-Lucie). 1664 - 16 Feb 1666 English occupation. 1667 - 1674 Administered by the French Compagnie des Indies Occidentales. 1674 French crown colony, as a dependency of Martinique (evacuated 1674/88-1719, 1720-22, 1723-44). 16 Dec 1722 - Jan 1723 English settlement at Petit Carenage, opposed by French. 1723 - 1744 Neutral territory agreed by Britain and France in the Treaty of Choc, but French settlers remain. 1744 French colony (Sainte-Lucie). 18 Oct 1748 - 1756 Declared Neutral territory by Treaty of Aix La Chapelle (French do not evacuate and island remains de facto a French possession). 25 Feb 1762 - 10 Feb 1763 British occupation. 28 Dec 1778 - 03 Jan 1784 British occupation. 04 Apr 1794 - 18 Jun 1795 British occupation. 25 May 1796 - 27 Mar 1802 British occupation. 25 Oct 1797 - 19 Apr 1801 Nominally organized as Lucie département of France (Saint Lucia and Tobago; not effected due to British occupation). 26 Sep 1802 - 21 Jun 1803 Restored to France. 21 Jun 1803 British colony (Saint Lucia). 30 May 1814 British possession confirmed. 1838 British crown colony. 1838 - 01 Jan 1960 Part of the Windward Islands colony (under Grenada). 03 Jan 1958 - 31 May 1962 Part of the Federation of the West Indies (under Trinidad and Tobago). 01 Mar 1967 Associated state 22 Feb 1979 Independence from Britain as Saint Lucia. |
|||||
|
|
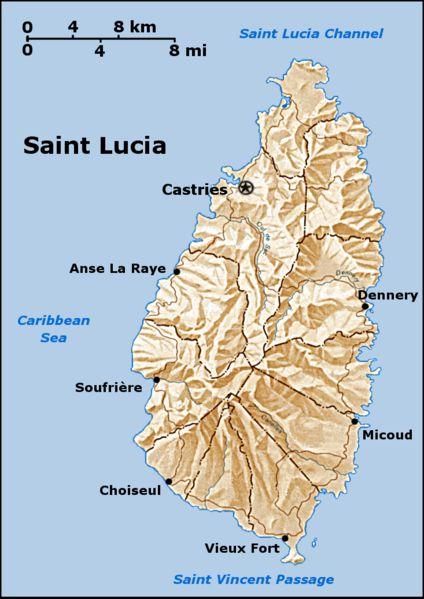
Saint Lucia, an independent island nation located in the Windward Islands of the West Indies. It is located north/northeast of Saint Vincent, northwest of Barbados and south of Martinique with an area of 617 km2 (238.23 sq mi). Capital: Castries (Le Carenage 1651-1785). The economy is agricultural. Bananas, copra, cocoa, sugar and logwood are exported. Columbus discovered Saint Lucia in 1502. The first attempts at settlement undertaken by the British in 1605 and 1638 were frustrated by sickness and the determined hostility of the fierce Carib inhabitants. The French settled it in 1650 and made a treaty with the natives. Saint Lucia was named after Saint Lucy of Syracuse by the French, the first European colonizers. English signed a treaty with the native Carib people in 1660. Territorial Dispute: Joins other Caribbean states to counter Venezuela's claim that Aves Island sustains human habitation, a criterion under UNCLOS, which permits Venezuela to extend its EEZ/continental shelf over a large portion of the Caribbean Sea. |
||||
| England took control of the island from 1663 to 1667; in ensuing years, it was at war with France 14 times and rule of the island changed frequently (it was seven times each ruled by the French and British). In 1814, the British took definitive control of the island. Because it switched so often between British and French control, Saint Lucia was also known as the "Helen of the West Indies". | |||||
| In 1967, under the West Indies Act, Saint Lucia was established as a British associated state, self-governing in internal affairs. Complete independence was attained on February 22, 1979. Saint Lucia is a member of the Commonwealth of Nations. Elizabeth II is Head of State as Queen of Saint Lucia. | |||||
| Two Nobel laureates, Arthur Lewis, an economist, and Derek Walcott, a poet and playwright, have come from the island. It is the nation with the second most such honorees per capita after the Faroe Islands. | |||||
|
|||||
|
Monetary standard:
East Caribbean Dollar = 100 cents.
Prior to 1950, the island used sterling, which was superseded by the currency of the British Caribbean Territories (Eastern Group) and the East Caribbean State. |
|||||
| The East Caribbean dollar (sign: $; code: XCD) is the currency of eight of the nine members of the Organisation of Eastern Caribbean States (the one exception being the British Virgin Islands). It has existed since 1965, being the successor to the British West Indies dollar, and it is normally abbreviated with the dollar sign $ or, alternatively, EC$ to distinguish it from other dollar-denominated currencies. The EC$ is subdivided into 100 cents. It has been pegged to the United States dollar since July 07, 1976 and the exchange rate is US$1 = EC$2.70. Six of the states using the EC$ are independent states: Antigua and Barbuda, Dominica, Grenada, Saint Kitts and Nevis, Saint Lucia, and Saint Vincent and the Grenadines. The other two are British overseas territories: Anguilla and Montserrat. Commemorative coins were produced by Saint Lucia in 1970, 1982, 1985, 1986 and 1988. | |||||
| Saint Lucia commemorative coins | |||||
|
|||||
| Countries / Territories | |||||
| Chiefa Coins | |||||