|
 |
| Saint Vincent and The Grenadines | |||||
 |
|
||||
|
22 Jan 1498 Discovered and claimed for Spain by Christopher Columbus, named Isla de San Vicente. 1627 - 1636 Claimed by England, unsettled. 1672 Claimed by England, unsettled. 1673 - 1762 Neutral territory (as agreed by England and France). c.1700 French settlers arrive (Saint-Vincent). Feb 1762 British occupation. 10 Feb 1763 British colony (subordinated to Grenada). 1776 British crown colony. 16 Jun 1779 - 03 Sep 1783 French occupation. 01 Apr 1833 - 01 Jan 1960 Part of the Windward Islands colony (see Grenada). 03 Jan 1958 - 31 May 1962 Part of the Federation of the West Indies (under Trinidad and Tobago). 27 Oct 1969 Associated state 27 Oct 1979 Independence (St. Vincent and the Grenadines). 22 Oct 1985 New flag adopted 25 Nov 2009 Republic constitution defeated in vote 55%-43%. |
|||||
|
|
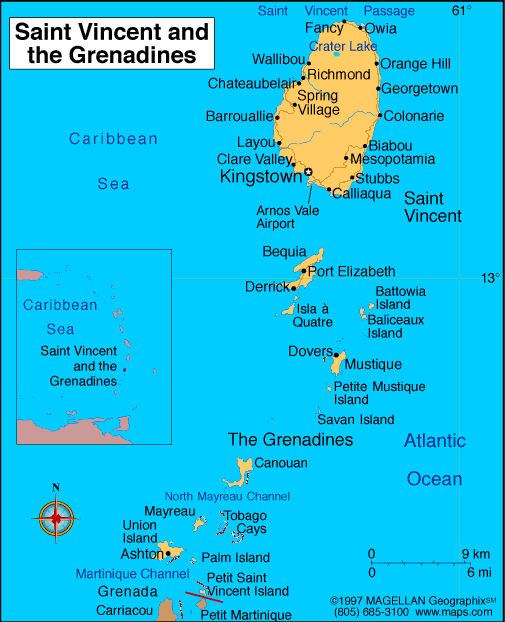
Saint Vincent and the Grenadines, consisting of the
island of Saint Vincent and the northern Grenadines (a string of islets
stretching southward from Saint Vincent), is located in the Windward Islands
of the West Indies, West of Barbados and south of Saint Lucia. The tiny
nation has an area of 150sq. mi. (340 sq. km.).
Capital:
Kingstown.
Motto: "Pax et Justitia"
(Latin) [translation in English: "Peace and Justice"].
Arrowroot, cotton, sugar, molasses, rum and cocoa are exported. Tourism is a principal industry. Saint Vincent was discovered by Columbus on Jan. 22,1498, but was left undisturbed for more than a century. The British began colonization early in the 18th century against bitter and prolonged Carib resistance. The island was taken by the French in 1779, but was restored to the British in 1783, at the end of the American Revolution. Saint Vincent and the northern Grenadines became a British associated state on 27 Oct. 1969. |
||||
| Independence under the name of Saint Vincent and the Grenadines was attained at midnight of Oct. 26, 1979. The new nation chose to become a member of the Commonwealth of Nations with Elizabeth II as Head of State and Queen of Saint Vincent. | |||||
| The main island of Saint Vincent measures 18 km (11 mi) long, 11 km (6.8 mi) in width and 344 km2 (133 sq mi) in area. From the most northern to the most southern points, the Grenadine islands belonging to Saint Vincent span 60.4 km (37.5 mi) with a combined area of 45 km2 (17 sq mi). Most of the nation lies within the Hurricane Belt. | |||||
| The island now known as Saint Vincent was originally named Hairoun ("The Land of the Blessed") by the native Caribs. The Caribs aggressively prevented European settlement on Saint Vincent until 1719. Prior to this, formerly enslaved Africans, who had either been shipwrecked or who had escaped from Barbados, Saint Lucia and Grenada and sought refuge in mainland Saint Vincent, intermarried with the Caribs and became known as Garifuna or Black Caribs. Beginning in 1719, French settlers from Martinique gained control of the island and began cultivating coffee, tobacco, indigo, cotton, and sugar on plantations. These plantations were worked by enslaved Africans. In 1763 by the Treaty of Paris, France ceded control of Saint Vincent to Britain, who began a program of colonial plantation development that was resisted by the Caribs. France captured the island in 1779, but the British then regained Saint Vincent for good under the Treaty of Versailles (1783). This treaty was an ancillary treaty to the Treaty of Paris (1783), through which Great Britain officially recognised the end of the American Revolutionary War. Between 1783 and 1796, there was again conflict between the British and the Black Caribs, who were led by defiant Paramount Chief Joseph Chatoyer. In 1797 British General Sir Ralph Abercromby put an end to the open conflict by crushing an uprising which had been supported by the French radical, Victor Hugues. More than 5,000 Black Caribs were eventually deported to Roatán, an island off the coast of Honduras. Slavery was abolished in Saint Vincent (as well as in the other British colonies) in 1834, and an apprenticeship period followed which ended in 1838. After its end, labour shortages on the plantations resulted, and this was initially addressed by the immigration of indentured servants. In the late 1840s many Portuguese immigrants arrived from Madeira and between 1861 and 1888 shiploads of East Indian labourers arrived. Conditions remained harsh for both former slaves and immigrant agricultural workers, as depressed world sugar prices kept the economy stagnant until the start of the 20th century. | |||||
|
|||||
|
Monetary standard:
East Caribbean Dollar = 100 cents.
A local coinage was introduced in 1797, with the gold withdrawn in 1818 and the silver in 1823. This was replaced by sterling. From the mid-1950's, Saint Vincent used the currency of the British Caribbean Territories (Eastern Group), then that of the East Caribbean States. |
|||||
| The East Caribbean dollar (sign: $; code: XCD) is the currency of eight of the nine members of the Organisation of Eastern Caribbean States (the one exception being the British Virgin Islands). It has existed since 1965, being the successor to the British West Indies dollar, and it is normally abbreviated with the dollar sign $ or, alternatively, EC$ to distinguish it from other dollar-denominated currencies. The EC$ is subdivided into 100 cents. It has been pegged to the United States dollar since July 07, 1976 and the exchange rate is US$1 = EC$2.70. Six of the states using the EC$ are independent states: Antigua and Barbuda, Dominica, Grenada, Saint Kitts and Nevis, Saint Lucia, and Saint Vincent and the Grenadines. The other two are British overseas territories: Anguilla and Montserrat. Commemorative coins were produced by Saint Lucia in 1970, 1985 and 1988. | |||||
| Saint Vincent and the Grenadines commemorative coins | |||||
|
|||||
| Countries / Territories | |||||
| Chiefa Coins | |||||